You might be tempted to settle for either the RX7600 or RTX4060, both of which come with 8 GB vRAM, thinking they’ll hold on for a few more years, but here’s the thing: They most likely won’t.
Just like the GTX 560 TI from Nvidia or the competing HD6870 from AMD from years ago that came with 1 GB vRAM and became more or less obsolete in less than two years, the same will prove to be true for 8 GB vRAM GPUs.
So, unless you’re looking for a temporary GPU or mainly interested in eSports gaming, it’s best to avoid GPUs with 8 GB vRAM in 2023.
If you’ve read this far and are wondering what all this vRAM technical mumbo-jumbo is, allow us to simplify things.
Does GPU Vram Matter for Gaming?
Absolutely. A GPU’s vRAM significantly impacts gaming performance; more vRAM allows a GPU to handle higher-quality textures, render greater distances, create better-quality shadows, and enable ray tracing, among other intensive graphical settings.
A GPU with low vRAM relies on the system memory instead, which tends to be much slower than GDDR vRAM and can negatively affect gaming performance.
Is 8 GB of VRAM Enough in 2023?
Unfortunately, no. 8 GB of vRAM is no longer enough, even for 1080p gaming, let alone 1440p or 4K. Recently released AAA titles like The Last of Us, Hogwarts Legacy, Resident Evil 4, and Ratchet & Clank – Rift Apart can easily consume up to 12 GB of VRAM at 1080p on medium to high graphics settings with ultra-quality textures.
So, purchase a card with enough vRAM to play these next-gen. AAA games with the in-game settings cranked to the max.
But how do you figure out how much vRAM you have? Well, let’s take a look:
How Much VRAM Do I Have?
Check out these three quick and easy ways to find out your GPU’s vRAM:
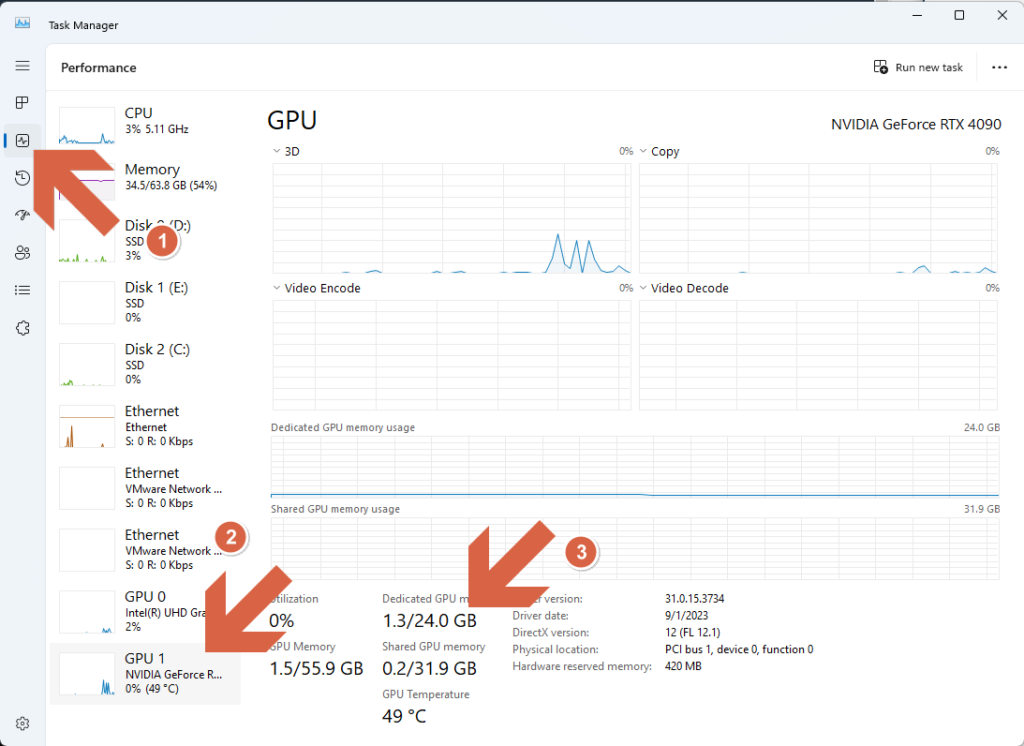
1. The easiest way is to use the Windows Task Manager. Start by right-clicking on the Task Bar at the bottom, choose ‘Task Manager,’ and under the ‘Performance’ tab, select “GPU 0.” Then, look to the bottom of the screen, and you’ll find your GPU’s memory, along with vRAM usage, mentioned under ‘Dedicated GPU Memory.’
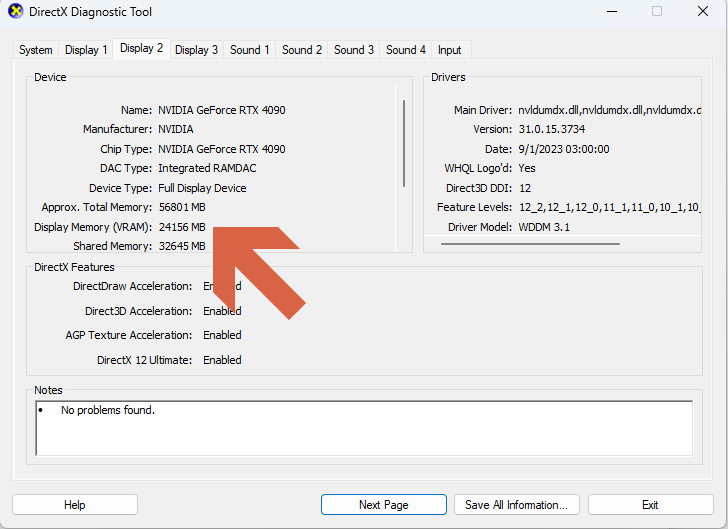
2. The second option involves using the DirectX Diagnostic Tool. Simply press ‘Windows + R’ to open the ‘Run’ command window. In the search box, type “DxDiag” and press Enter. In the DirectX Diagnostic Tool window, click ‘Display,’ and under ‘Devices,’ locate ‘Display Memory’ to find your GPU’s vRAM capacity.
3. Lastly, you can download, install and run GPU-Z. It’s a program that gives you a detailed list of all your GPU’s specifications, including its memory size, type, bus width, and peak bandwidth.

How Much VRAM Do I Need for Gaming?
If you have a 1080p monitor, you’ll need at least 12 GB of vRAM, if not more, to run recently released AAA titles and future-proof your graphics card for upcoming games with increasingly higher-quality textures. In the case of 1440p, the sweet spot is 12 to 16 GB, especially if you’re interested in Ray Tracing (which requires additional vRAM).
Lastly, for 4K or higher resolutions, the more vRAM, the merrier, as these resolutions are very vRAM intensive and can strain even the most powerful GPUs. Aim for a GPU with at least 16 GB of VRAM for 4K gaming, if not 24GB, just to be safe.
But vRAM isn’t the only factor to consider when purchasing a new graphics card. A GPU is essentially a mini-computer in itself with its very own processing cores, cache, and, of course, vRAM designed specifically for graphics processing.
The following are all the specs worth considering before purchasing a GPU:
Shader Cores
Shader cores are responsible for processing 3D pixel and vertex shaders, tessellation, temporal anti-aliasing (TAA), and geometric shading.
Modern GPUs come with thousands of shader cores, and having more of them usually results in higher frame rates. That’s because computer graphics are highly parallel and scale well across multiple cores.
Choosing the GPU with the highest number of shader cores is always preferable for gamers. Ensure your computer case has adequate cooling, as more shader cores translate to more heat.
Render Output Units (ROPs)
ROPs sit at the very end of the rendering pipeline, producing the final pixels on the frame buffer, which is then displayed on your monitor.
They are connected directly to the on-die memory controllers and handle tasks like anti-aliasing (excluding TAA), post-process effects (bokeh, depth of field, FXAA, SMAA, etc.), delta color compression, anisotropic filtering, and determine the overall pixel throughput of the GPU.
Similar to shader cores, it’s a good idea to pick a GPU with as many ROPs as you can get. This is particularly important if you have a high-resolution monitor because higher resolutions require higher pixel throughput.
Memory Bus
The memory bus width determines the GPUs overall bandwidth and vRAM capacity. For example, 32-bit GDDR6 vRAM from HK Hynix and Samsung are available in 8Gb and 16Gb capacities. That means on a 256-bit wide bus, you can have either 8 or 16 GB of vRAM but not 10, 12, or 14GB.
Although a wider bus can offer improved overall bandwidth, the same can’t be said for performance because that depends on another important factor: Cache.
Cache
Both Nvidia and AMD are narrowing down their GPUs’ bus widths due to increasing DRAM prices. For example, the RTX3080 had a 320-bit bus, but its successor, the 4080, relies on a much smaller 256-bit bus.
Despite that, the 4080 delivers roughly 50% better performance than the 3080 on average because of its large L2 cache buffer.
The RTX3080’s GA102 chip had a 5 MB L2 cache, whereas the 4080’s AD103 has a 64 MB L2 cache, a massive difference. Such a large on-die SRAM reduces the GPU’s reliance on memory controllers and adjacent DRAM chips, which not only saves power but also dramatically reduces latency and, in turn, improves frame rate.
So, if you’re a gamer, it’s necessary to consider the bus width and cache capacity before purchasing a new GPU.
Now, let’s take a quick look at some of the most popular and graphically intensive games and how much vRAM they require for a smooth gaming experience:
| Game | 4GB | 8GB | 10GB | 12GB | 16GB | 24GB |
| The Last of Us | 720p | 900p | 1080p | 1440p | 4K | 8K |
| Ratchet & Clank – Rift Apart | 720p | 900p | 1080p | 4K | 8K | |
| Hogwarts Legacy | 720p | 900p | 1080p | 1440p | 4K | |
| Resident Evil 4 Remake | 720p | 1080p | 1440p | 4K | 8K | |
| Mass Effect Legendary Edition | 1080p | 1440p | 4K | 8K | 16K | |
| Counter Strike: Global Offensive | 1080p | 1440p | 4K | 8K | ||
| DOTA 2 | 1440p | 4K | 8K | 16K | ||
| Starcraft 2 – Wings of Liberty | 1440p | 4K | 8K | 16K | ||
| PUBG | 1080p | 1440p | 4K | 8K | ||
| Fortnite | 1080p | 1440p | 4K | 8K | ||
| Call of Duty: Warzone 2.0 | 720p | 1080p | 1440p | 4K | ||
| Overwatch | 900p | 1080p | 1440p | 4K | ||
| Cyberpunk 2077 | 900p | 1080p | 1440p | 4K | ||
Does VRAM Matter for Video Editing?
vRAM plays a role in video editing but on a more limited scale than gaming. That’s because most video editing programs rely mainly on the GPU’s compute units, such as CUDA and OpenCL, and use vRAM merely as a frame buffer for video playback. So, when it comes to 4K video editing using programs like Adobe Premiere Pro, 6 to 8 GB of vRAM is usually sufficient.
FAQs
Read on to find answers to some of the most commonly asked vRAM questions.
Is 32 GB vRAM Overkill?
Yes, having 32 GB of vRAM would be overkill for gaming, even when playing at 4K resolution. That said, it could come in handy at 8K resolution, which has a much higher pixel density of 33.17 megapixels, about 300% more than 4K, which stands at 8.3 megapixels.
How Much vRAM does RTX 3060 Have?
RTX3060 for desktop has three variants: 6 GB, 8 GB, and 12 GB vRAM configurations. The 6 GB and 12 GB versions share the same 192-bit bus, while the 8 GB version uses a narrower 128-bit bus with a lower memory bandwidth. Lastly, the RTX 3060 Mobile for laptops has a single configuration with 6 GB of vRAM on a 192-bit wide bus.
What Happens if vRAM Is Too High?
Having too much vRAM doesn’t affect performance. At most, the system will allocate more vRAM to the game, which may reduce minor hiccups and stutters in gameplay, potentially improving 1% and 0.1% frame time lows. However, the average FPS remains largely unaffected.
Is 64 GB vRAM Overkill for Gaming in 2023?
Yes, having 64 GB of vRAM is way overkill for gaming in 2023, even at 8K resolution. This massive amount of vRAM is currently limited to Nvidia’s Hopper line of professional A.I compute GPUs, which feature HBM2e memory with up to a 5,120-bit wide bus. This starkly contrasts consumer gaming GPUs, which traditionally feature GDDR memory with up to a 512-bit wide bus.
The Conclusion
To conclude, game vRAM requirements have surged exponentially because modern games now support the current-generation PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X consoles, which are significantly more powerful than their predecessors.
A GPU with 8 GB vRAM used to be more than enough even for 1440p gaming, but now it struggles to support stable frame rates for demanding games at 1080p.
So, if you’re looking to upgrade to a GPU that will keep you without any issues for a few years, selecting the right amount of vRAM based on your monitor’s resolution.
For 1080p gaming, especially with Ray Tracing, it’s essential to consider a GPU with at least 12 GB of vRAM. If you’re gaming at 1440p, you should aim for 16 GB, whereas in the case of a 4K monitor, we recommend a GPU with at least 16 GB of vRAM, if not more.
This brings us to the end of our vRAM discussion. To learn more about gaming in 2023, check out our How Much Is a Good Gaming PC blog to save hundreds of dollars!

